mai tech
Friday, 30 December 2016
Monday, 5 December 2016
Image processing project list
Image processing project list
1. Nonlocal casual Walks Algorithm for partially usual 2D-to-3D icon translation
2. Risky Willpower of Frequent Experimental RGB-D Representations Formed on Nonlocal Return and Complete Variance
3. A 3D Entity Descriptor Greater from an Exact 2D Integrity design Synthetic Water Level Controller using Arduino
4. Shade Image Blur Estimation via Cavernous Learning
5. Optimized Multi operator Image Retargeting Based on Perceptual Similarity Measure
6. Rank based Image Watermarking Method with High Embedding Capacity and Robustness
7. Real-time Semantic Search using Approximate Methodology for Large-scale Storage Systems
8. Sparse Contextual Activation for Efficient Visual Re-ranking
9. Reversible Data Hiding in Encrypted Images by Reversible Image Transformation
10. Online Multi-modal Distance Metric Learning with Application to Image Retrieval
11. On the Security of Permutation-Only Image Encryption Schemes
12. Adaptive Reversible Data Hiding by Extending the Generalized Integer Transformation
13. Combining Left and Right Palm-print Images for More Accurate Personal Identification
14. Learning Compact Binary Face Descriptor for Face Recognition
15. Localized Multi-Feature Metric Learning for Image Set Based Face Recognition
16. Multi-scale Logarithm Difference Edge-maps for Face Recognition Against Varying Lighting Conditions
17. Iterative Vessel Segmentation of Fundus Images
18. Content Based Image Retrieval by Metric Learning from Radiology Reports Application to Interstitial Lung Diseases
19. EMR A Scalable Graph-based Ranking Model for Content-based Image Retrieval
20. Content-Based Image Retrieval Using Error Diffusion Block Truncation Coding Features
21. Local Diagonal Extreme Pattern A New and Efficient Feature Descriptor for CT Image Retrieval
best audrino final year project lists
Audrino project list
- Gas Leakage Detector with GSM Module for SMS Alert and Sound Alarm
- PIR Sensor Burglar Alarm with SMS Alert and Sound Alarm using Arduino
- Gestured Controlled Smart Home
- Temperature Logger using Arduino
- Water Level Controller using Arduino
- Ultrasonic Range Finder using Arduino
- Advanced Digital Code Lock using Arduino
- Digital Thermometer using Arduino
- LPG Leakage Detector
- Smoke Detection using MQ-2 Gas Sensor
- Interfacing Gyroscope to Arduino
- Arduino Automatic Temperature& Humidity Controller
- Arduino Automatic Watering System For Plants Sprinkler
- Arduino Automatic Watering System
- Arduino Barometric Pressure Web Server
- Ultrasonic Map-Maker using an Arduino Yun
- Arduino Based Auto Timer
- Arduino Based Automated Lighting Control
- Arduino based Bi-color LED Matrix Audio
Spectrum Visualizer
- Arduino based Distance Sensor
- Arduino based Electronic Queuing System
- Non-Intrusive Elderly Smart Home (NESH)
- Arduino based IR Remote Control Robot
- Arduino Based Security System using GSM
& PIR Sensor
- Arduino Control DC Motor via Bluetooth\
- Arduino controlled webcam panner
- Arduino Fixed-point Vehicle Proximity
Detector
- Arduino GPS Tracking System
- Arduino home energy monitor shield
- Arduino based reef controller
- Intelligent Charger for V NiMH
Rechargeable Batteries
- Robot car Controlled Using G-Sensor
Smartphone
- IoT
PCR: Low Cost DNA Replication Connected to the Internet
- Speed and Direction Control of DC Motor
using Arduino
- GSM
Based Home Security Alarm System Using Arduino
- Arduino Based Auto Intensity Control Of
Street Lights
- Arduino Based Autopilot System
- Arduino Based Battery Charge
- Arduino Based Car Parking System
- Arduino Based Energy Meter
- Arduino Based Flight Controller For
Quadcopter
- Arduino Based Intervalometer
- Arduino Based Health Monitor
- Arduino Based Tilt Detector
- Arduino Based Underground Cable Fault
Detection
- Arduino Night Security Alarm With PIR
Sensor
- Brainwave Powered Prosthetic Arm By
Arduino
- Arduino based Breathalyzer Microphone
- Detect A Knock On A Sensor (Knock)
- Garduino-Automated Gardening System
- High Speed Photography Using The Arduino
- Low-Cost Global Satellite Signaling With
Iridium
- Weather Station Receiver using Arduino
- Arduino VFO - a Direct Digital Synthesis
Radio-Frequency generator on the Arduino platform
- Accident Detection and Messaging System
using GSM and GPS
- Green House Monitoring using Arduino
- Antenna Tracking System for Airborne
Vehicles in UHF Communication Range
- Arduino Based Wireless Notice Board -
Send Notice Using Your Cell Phone
- Angle and Distance Measurement Device
using Arduino
- Flashlight Controlled Solar Powered Robot
using Arduino
- Solar Panel Parameters Monitoring Using
Arduino
- Traffic Surveillance System using MATLAB
and Arduino
- Arduino Traffic Light Controller with
Remote Control
- Arduino Controlled Digital Window Sticker
- Arduino Processing Audio Spectrum
Analyzer
- Arduino Keyboard and Mouse Control Code
- Build a Complete AVR System and Play
Mastermind using Arduino
- Autonomous Auto-navigation Robot using
Arduino
- Analog audio panel for PC using Arduino
- Analog audio panel for PC using Arduino
- Visual Network Threat Level Indicator v
using Arduino
- A
Study in Non-Standard Distributed Computer Architecture using Arduino
- Using an Arduino to Control an Infrared
Helicopter
- Secret Knock Detecting Door Lock using
Arduino
- Google Weather on graphical display with
Arduino
- Arduino based Electrical Appliances
Control using IR
- Low
cost Thermal Monitoring System for Processor Core using RTOS
- Algorithm for increasing the efficiency
of Energy Management in WSN based on RTOS
- EEG
based Attention Tracking during Distracted Driving
- Analysis
and Simulation of Brain Signal Data by EEG Signal Processing Technique
using Matlab
- Mind-Controlled Wheelchair using an EEG
Headset
- Parallel Monitoring for the Next
Generation of Train Control Systems
- Distributed Smart Sensing Systems for
Stratospheric Ozone Depletion
pls leave a comment
what is resistor - how it works - how to check the resistor value
Resistor

Resistor is a passive two terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element.
In electronics circuits , resistor are used to reduce current flow , adjust signal levels , to divide voltages , bias active elements , and terminate transmission lines , among other uses.
High-power resistors that can dissipate many watts of electrical power as heat may be as part of motor controls , in power distribution systems , or as test loads for generators .
Fixed resistors have resistances that only change slightly with temperature, time or operating voltage. Variable resistors can be used to adjust circuit elements (such as a volume control or a lamp dimmer), or as sensing devices for heat, light, humidity, force, or chemical activity.
- resistor value can be checked by using color code
- and also can be checked by using multi meter
- for begineers multi meter is very useful
What is diode and how its work - simple circuits and tutorial
Diode
A diode is a device which only allows unidirectional flow from positive direction to negative direction.
A diode only blocks current in the reverse direction while the reverse voltage is within a limited range otherwise reverse barrier breaks and the voltage at which this breakdown occurs is called reverse breakdown voltage. The diode acts as a valve in the electronic and electrical circuit. A P-N junction is the simplest form of the diode which behaves as ideally short circuit when it is in forward biased and behaves as ideally open circuit when it is in the reverse biased. Beside simple PN junction diodes, there are different types of diodes although the fundamental principle is more or less same. So a particular arrangement of diodes can convert AC to pulsating DC, and hence, it is sometimes also called as a rectifier. The name diode is derived from "di-ode" which means a device having two electrodes. Its also used to convert from AC to DC current.
Types of Diode
The types of diode are as follow-- Zener diode
- P-N junction diode
- Tunnel diode
- Varractor diode
- Schottky diode
- Photo diode
- PIN diode
- Laser diode
- Avalanche diode
- Light emitting diode
Simple circuit for diode:
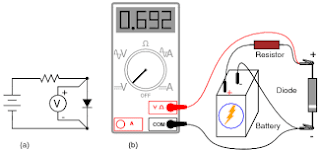
how to check that the diode is working or not:
- Using multimeter we can check the diode
- if the multimeter display any value then the diode is working condition
- and some thersold values are there to check the diode is working properly or not
- below picture shows that how to check the diode
555 timer - how its works - simple and easy tutorial
555 timer
| Pin | Name | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | GND | Ground reference voltage, low level (0 V) |
| 2 | TRIG | Output of the timer totally depends upon the amplitude of the external trigger voltage applied to this pin. |
| 3 | OUT | This output is driven to approximately 1.7 V below +VCC, or to GND. |
| 4 | RESET | A timing interval may be reset by driving this input to GND, but the timing does not begin again until RESET rises above approximately 0.7 volts. Overrides TRIG which overrides THR. |
| 5 | CTRL | Provides "control" access to the internal voltage divider (by default, 2/3 VCC). |
| 6 | THR | The timing (OUT high) interval ends when the voltage at THR ("threshold") is greater than that at CTRL (2/3 VCC if CTRL is open). |
| 7 | DIS | Open collector output which may discharge a capacitor between intervals. In phase with output. |
| 8 | VCC | Positive supply voltage, which is usually between 3 and 15 V depending on the variation. |
The IC 555 has three operating modes:
- Bistable mode or Schmitt trigger – the 555 can operate as a flip-flop, if the DIS pin is not connected and no capacitor is used. Uses include bounce-free latched switches.
- Monostable mode – in this mode, the 555 functions as a "one-shot" pulse generator. Applications include timers, missing pulse detection, bounce-free switches, touch switches, frequency divider, capacitance measurement, pulse-width modulation (PWM) and so on.
- Astable (free-running) mode – the 555 can operate as an electronic oscillator. Uses include LED and lamp flashers, pulse generation, logic clocks, tone generation, security alarms, pulse position modulation and so on. The 555 can be used as a simple ADC, converting an analog value to a pulse length (e.g., selecting a thermistor as timing resistor allows the use of the 555 in a temperature sensor and the period of the output pulse is determined by the temperature). The use of a microprocessor-based circuit can then convert the pulse period to temperature, linearize it and even provide calibration means.
Bistable Mode :
circuit diagram for bistable mode
The 555 timer in bistable mode is also known as a flip-flop circuit. A flip-flop circuit alternates between two stable states, in this case the output of electrical current from the output pin. This is a fairly basic 555 timer circuit and unlike monostable mode and astable mode, it does not depend on a resistor and capacitor to set the timing of the circuit. In fact there is no timing in this circuit. There are only two stable states (on and off) controlled directly by the trigger pin and reset pin.
monostable mode:
circuit diagram
This is the circuit diagram of 555 Timer wired in Monostable mode. 8th pin and 1st pin of the 555 timer are used to given power Vcc and Ground respectively. 4th pin is the Reset pin of 555 Timer, which is active low so it is connected to Vcc to avoid accidental resets. 5th pin is the Control Voltage pin used to provide external reference voltage to internal comparators. Since it is not used here, it is grounded via a capacitor C’ (0.01µF) to avoid high frequency noises. When a negative trigger is applied on the Trigger input of 555, output goes high and capacitor starts charging through resistor R. When the capacitor voltage becomes greater than 2/3 Vcc, ouput goes low and capacitor starts discharging through the Discharge pin of 555 Timer. Time period of the unstable state is given the tye expression, T = 1.1RC.
Astable mode :
circuit diagram
The astable configuration, with two resistors, cannot produce a 50% duty cycle. To produce a 50% duty cycle, eliminate R1, disconnect pin 7 and connect the supply end of R2 to pin 3, the output pin. This circuit is similar to using an inverter gate as an oscillator, but with fewer components than the astable configuration, and a much higher power output than a TTL or CMOS gate. The duty cycle for either the 555 or inverter-gate timer will not be precisely 50% due to the fact the timing network is supplied from the devices output pin, which has different internal resistances depending on whether it is in the high or low state (high side drivers tend to be more resistive).it will create 0 and 1's pulse rate as output.
circuit diagram
The astable configuration, with two resistors, cannot produce a 50% duty cycle. To produce a 50% duty cycle, eliminate R1, disconnect pin 7 and connect the supply end of R2 to pin 3, the output pin. This circuit is similar to using an inverter gate as an oscillator, but with fewer components than the astable configuration, and a much higher power output than a TTL or CMOS gate. The duty cycle for either the 555 or inverter-gate timer will not be precisely 50% due to the fact the timing network is supplied from the devices output pin, which has different internal resistances depending on whether it is in the high or low state (high side drivers tend to be more resistive).it will create 0 and 1's pulse rate as output.
IRF830 traic - how it works_tutorial
IRF830
1) It's a type of transistor only
2) Its mainly used for dimming the ac appilances
for eg light,fan...
3) i dont want to explain deeply ,it will confuse you
4) pin(1) gate is a trigger pin ,when the trigger pin is triggered by some minimum voltage either by audrino's analog pin using ic(4n32) or some other optocoupler.
5) the triac will activated .
6) the property of IRF830 ,drain(2) is a negative pole and source(3) pin is a positive pole.
7) but the circuit is connected by negative for source(3) and positive for drain(2).
8) because the traic will not make a closed loop when there is no power supply(by its oposite pole).
9) i done a dimmer light circuit using IRF830
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)